impf-info.de
HPV - Desillusionierende Daten zu Prävalenz und Impfstoff-Effektivität vom RKI
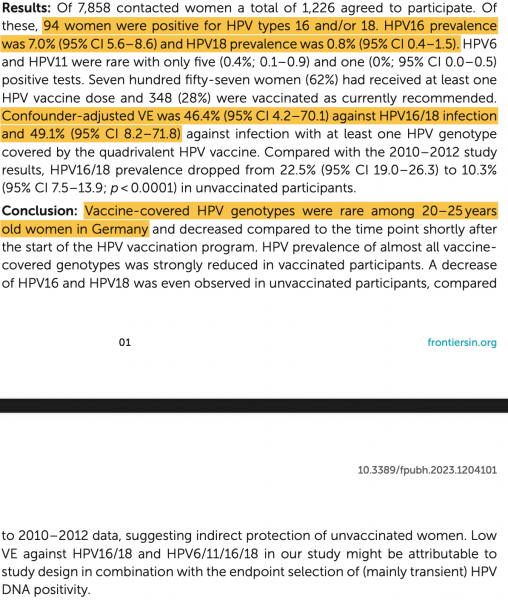
Eine mittelgroße Studie (N= 1226) mit jungen Frauen zwischen 20 und 25 Jahren aus D ergab beruhigende und enttäuschende Daten zu Infektionshäufigkeit mit und Impfstoff-Effektivität gegen HPV:
Beruhigend, weil die Prävalenz der im HPV-Impfstoff enthaltenen Serotypen bei jungen Frauen in D auch ohne Impfung niedrig ist: selbst bei den Hochrisiko-HPV-Typen 16/18 lag die Prävalenz bei maximal 7% und dies in einem Alter, in dem die Mehrzahl der Studienteilnehmerinnen bereits sexuellen Kontakt gehabt haben dürften.
Enttäuschend, weil diese Prävalenz durch die Impfung zwar tendentiell verringert wird, die Vertrauensbereiche der jeweiligen Häufigkeiten sich aber überlappen, was die wissenschaftliche Belastbarkeit dieses Umstandes kompromittiert.
Enttäuschend auch, weil die sich hieraus ergebende Impfstoff-Effektivität gegen eine Infektion mit den Hochrisiko-HPV-Typen 16/18 mit 46,4% (und absurd großem Vertrauensbereich von 4,2 - 70,1) spürbar unter 50% liegt - der allgemeinen Marke für eine relevante klinische Wirksamkeit von Impfstoffen.
Wie aus diesen Daten eine Bestätigung der STIKO-Impfempfehlung abgeleitet werden kann, die erstens junge Mädchen weit vor Beginn der sexuellen Aktivität erfasst und zweitens unverändert (und wissenschaftlich überholt) an mehreren Impfdosen festhält, bleibt ein Geheimnis der Autoren...
Frontiers | Human papillomavirus prevalence and vaccine effectiveness in young women in Germany, 2017/2018: results from a nationwide study
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://impf-info.de/